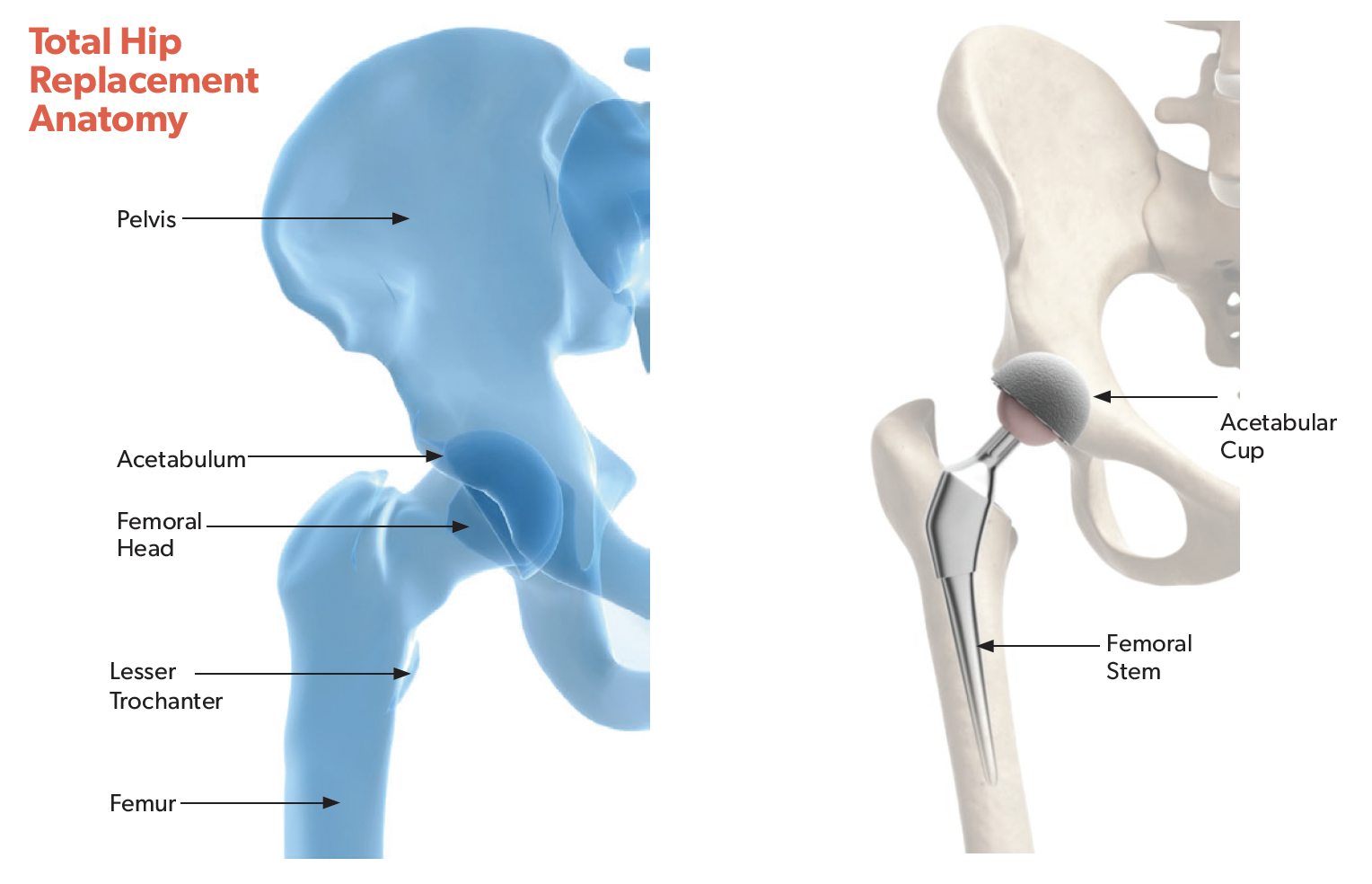
Total hip replacement involves replacing the joint with metal and plastic components. There are three basic parts to hip replacement:
1. Acetabular cup – a metal shell with a plastic liner that is placed into your hip socket
2. Femoral head (ball) – a component that attaches onto the stem and rotates like a natural hip in the hip socket; it may be made out of metal or ceramic
3. Femoral stem – a metal shaft that is inserted into your thighbone
There are different surgical approaches to hip replacement surgery
1. Posterior approach
2. Anterior approach
3. Anterior lateral approach
4. Direct Superior Approach
Your orthopedic surgeon will select the type of prothesis and its method of insertion/approach based on your age, activity level, bone quality and anatomy.